
What Happens to PV Panels When Their Life Cycle Ends
The energy industry has been experiencing a radical change and the gradual shift towards renewable energy sourcing is more than evident. Nevertheless, not all that looks sustainable stays that way upon the end of its life cycle. At least that is the most common worry regarding photovoltaic (PV) solar panels. They are a sustainable source of energy, dependant only on solar radiation, and capable of delivering electricity to our homes. However, what happens to solar panels when they fail to perform efficiently? Explore their journey through the recycling process in the infographic below:
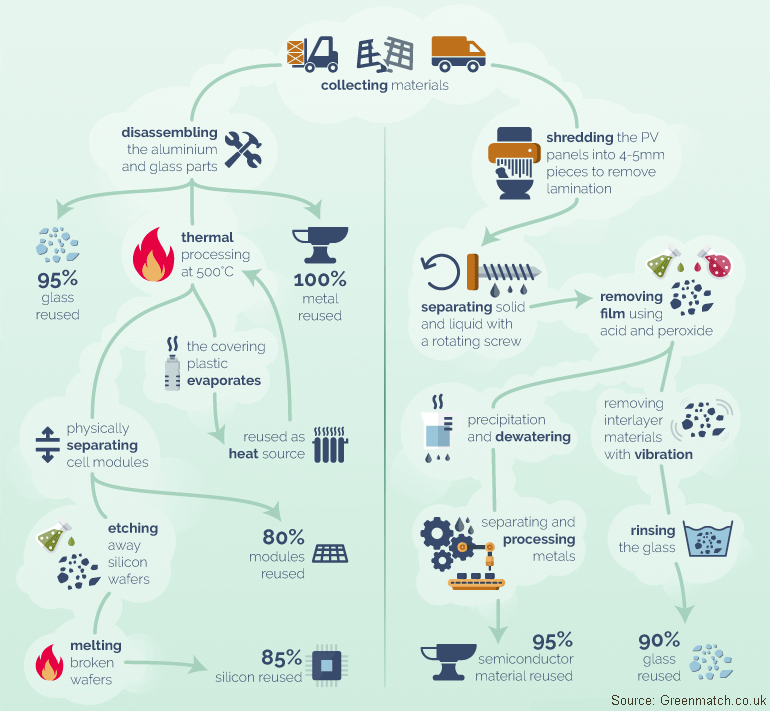
Solar Panel Recycling Processes
There are two main types of solar panels, requiring different recycling approaches. Both types-silicon based and thin-film based-can be recycled using distinct industrial processes. Currently, silicon based panels are more common, though that does not mean that there would not be great value in the materials of thin-film based cells.
Research studies conducted on the topic of recycling solar panels have resulted in numerous technologies. Some of them even reach an astonishing 96% recycling efficiency, but the aim is to raise the bar higher in the future.
Silicon Based Solar Panel Recycling
The recycling process of silicon-based PV panels starts with disassembling the actual product to separate aluminium and glass parts. Almost all (95%) of the glass can be reused, while all external metal parts are used for re-molding cell frames. The remainder materials are treated at 500C in a thermal processing unit in order to ease up the binding between the cell elements. Due to the extreme heat, the encapsulating plastic evaporates, leaving the silicon cells ready to be further processed. The supporting technology ensures that not even this plastic is wasted, therefore it is reused as a heat source for further thermal processing.
After the thermal treatment, the green hardware is physically separated. 80% of these can readily be reused, while the remainder is further refined. Silicon particles-called wafers-are etched away using acid. Broken wafers are melted to be used again for manufacturing new silicon modules, resulting in 85% recycling rate of the silicon material.
Thin-Film Based Solar Panel Recycling
In comparison, thin-film based panels are processed more drastically. The first step is to put them in a shredder. Afterwards, a hammermill ensures that all particles are no larger than 4-5mm, which is the size where the lamination keeping the inside materials together breaks, and hence can be removed. Contrary to silicon-based PV panels, the remaining substance consists of both solid and liquid material. To separate these, a rotating screw is utilised, which basically keeps the solid parts rotating inside a tube, while the liquid drips into a container.
Liquids go through a precipitation and dewatering process to ensure purity. The resulting substance goes through metal processing to completely separate the different semiconductor materials. The latter step depends on the actual technology used when producing the panels; however, on average 95% of the semiconductor material is reused.

